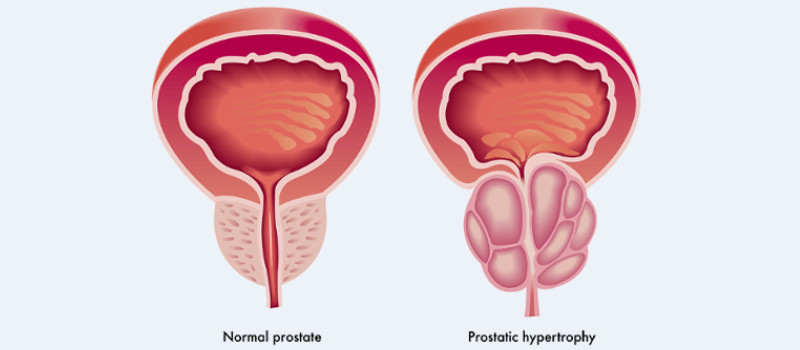
Prostate Enlargement
What is Prostatic Enlargement?
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland that forms part of the male
reproductive system. The gland is made of two lobes enclosed by an
outer layer of issue. The prostate is located in front of the rectum
and just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the canal through
which urine passes out of the body.
Enlarged Prostate
Though the prostate continues to grow during most of a man's life,
the enlargement doesn't usually cause problems until late in life.
BPH rarely causes symptoms before age 40, but more than half of men
in their sixties and as many as 90 percent in their seventies and
eighties have some symptoms of prostate enlargement.
What are the symptoms?
-
33% of the people above 60 yrs are affected by it.
-
Symptoms can be : Obstructive symptoms such as hesitancy, having
to strain to pass urine, weak stream, sense of incomplete
evacuation.
-
Irritative symptoms: frequency of urination, urgency and urge
incontinence leakage of urine before reaching toilet.
What Complication Can Occur If Not Treated?
-
Acute urinary retention (AUR) ( sudden painful inability to urinate).
The patients will need a catheter to drain the urine
-
Urinary tract infections (UTI) ( painful urination.)
-
Bladder stones, These are mineral deposits that can cause infection,
bladder irritation, blood in the urine and obstruction of
urine flow.
-
Bladder damage, where the bladder may loose its capacity to contract
which function may not be recovered in the elderly even after
surgery.
-
Kidney damage, ( hydronephrosis, swelling (dilation) of the urine-collecting
structures in one or both kidneys and may lead to inability of kidney
to remove waste products in the body causing permanent kidney.
Does Size Matter?
-
The size of the prostate does not always determine how severe
the obstruction or the symptoms will be. Some men with greatly
enlarged glands have little obstruction and few symptoms while
others, whose glands are less enlarged, have more blockage and
greater problems In general larger the size of the gland, there
is increased risk of symptoms and urinary retention (Stoppage of
urination requiring catheter drainage).
-
Clinical examination of prostate and PSA blood
test are required to detect and treat early prostate cancer.
-
Annual PSA is a must person over the age of 60 years.
-
Medical treatment is very effective in the early
stages of BPH when symptoms are mild and no complications have
developed. Side effects are very minimal and even very elderly
patients tolerate medications very well. It is very important
to come for regular checkup which can confirm that treatment is
effective and any complications can be detected early.
When is surgery required?
Surgery is required when medical treatment is not effective and or
complications have developed such as complete blockage of urine
(Retention of urine ), recurrent urinary tract infection, passing of
blood in the urine , reduction in kidney function, bladder stone, large
bladder diverticulum (out-pouching from bladder).
Can prostate re grow after prostate surgery?
-
In endoscopic surgery of prostate , part of the prostate blockage
called adenoma is removed and shell of part remains . This can
regrow and can cause further problem in 5 to 7% of cases.
-
Similarly prostate cancer can develop with in the shell of prostate
remaining. Annual PSA blood check and digital rectal examination
of prostate is a must.
What is laser prostate surgery?
It is called Laser Enucleation of prostate using Holium laser ( HOLEP).
Surgical Treatment for Prostate Enlargement
Enlarged Prostate (Adenoma) removal is done through urethral passage.
It is called Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP). Common methods
are called Mono polar TURP and Bipolar TURP. Most modern and more
effective procedure is done using Laser.
How is the procedure done ?
-
Procedure is done through natural passage ( Urethra).
-
Patient’s fitness is assessed by physician, cardiologist and Anesthetist
before admission. Endoscopy is passed to check the urethra, Bladder and
Prostate.
-
Special instrument called resectoscope is passed which has a channel to pass
laser fibre. Most powerful 100 watts Holmium laser is used. Prostate is
enucleated and then it is broken into small pieces using a morcellator.
-
A catheter is placed to drain the urine and is usually removed
24 hours later.
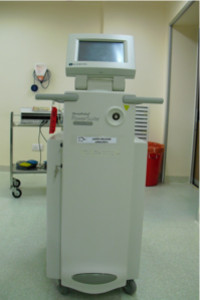
Laser Machine
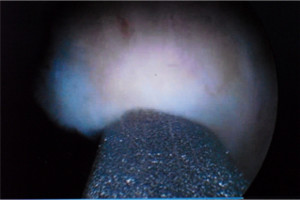
Prostate being morsellated
Removed Prostate
It Offers Many Advantages :
-
Painless procedure, no blood loss.
-
Safe in elderly, cardiac patients and those taking blood thinners.
-
Smooth recovery, early discharge.
-
patient can return to work early.
What to expect after surgery?
-
Initially urinary frequency, urgency can be present and usually
settles in few days.
-
Very small percentage of patients may experience mild stress leak which
settles in few days.
Diabates and Benign Enlarged Prostate :
-
Diabetics are prone to reduced contraction of bladder wall an this
leads to inefficient emptying of urine from the bladder. Ultimately
these patients can retain more urine and surgery at that stage will
not give good result.
-
Endoscopic Laser prostate surgery is advised early
in Diabetics with residual urine to get good results after
surgery.